Class 12 History – Chapter 1: Bricks, Beads and Bones Final Exam-Oriented Notes
Class 12 History – Chapter 1
Bricks, Beads and Bones (The Harappan Civilization)
Key Points
- Town Planning
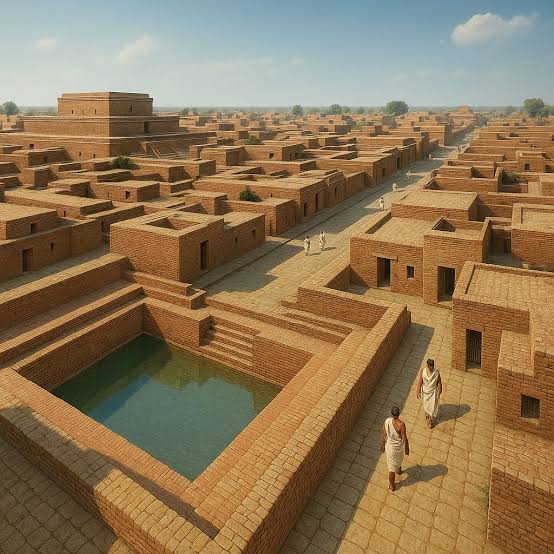

a. Well-planned grid system with streets cutting at right angles.
b. Division of city into Citadel (for ruling class, granaries, assembly halls) and Lower Town (residential area).
c. Houses made of standardized burnt bricks.
2. Drainage System

a) Advanced underground drainage made of baked bricks.
b) Each house connected with main drains.
c) Covered drains with regular cleaning arrangements.
3. Craft Production

a) Specialized production of beads, bangles, ornaments, seals, pottery.
b) Raw materials like carnelian, chert, steatite, lapis lazuli, copper, gold.
c) Evidence from Chanhudaro (craft production center).
4. Harappan Script

a) Written on seals, pottery, copper tablets.
b) Still undeciphered.
c) Contains short inscriptions with symbols (pictographic in nature).
5. Decline of Harappan Civilization
- Around 1900 BCE onwards.
- Multiple theories: climate change, drying of rivers (Saraswati), deforestation, floods, decline of trade, invasion.
- Urban centres declined, but rural life continued.
6) Archaeologists – Cunningham & Marshall
- Alexander Cunningham (1870s):

First identified Harappa but mistook it as Buddhist site.
John Marshall (1920s):

a) Announced discovery of Harappa & Mohenjodaro as civilization.
b) Later excavations by R.D. Banerjee, Daya Ram Sahni, Mortimer Wheeler.
7. Food & Agriculture

a) Wheat, barley, rice, peas, sesame, millets cultivated.
b) Evidence of irrigation and plough-based farming (Kalimangan).
c) Domestication of animals: cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, elephant, camel.
8. Trade & Commerce
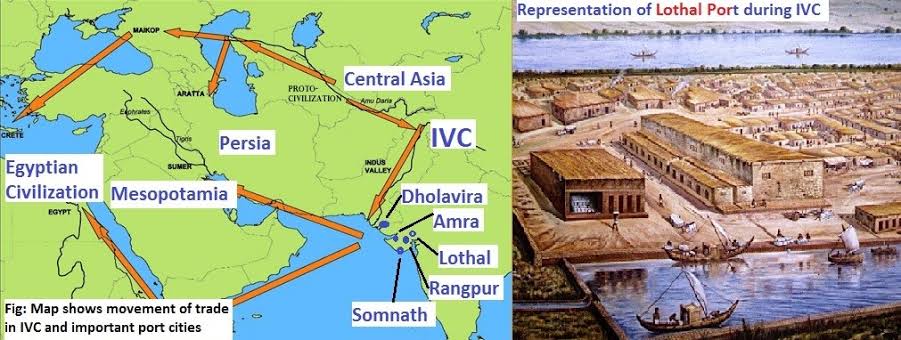
- Inland trade with Rajasthan, Gujarat, Deccan.
- Foreign trade with Mesopotamia (Meluhha).
- Export of beads, textiles, cotton, precious stones. Import of copper, tin, silver.
9. Religion & Seals

- Seals: made of steatite, used for trade and identification.
- Religious symbols: Pashupati seal, Mother Goddess figurines, worship of nature (trees, animals).
- No large temples found.
10. Political Life

- No evidence of kings or palaces.
- Uniformity in weights, measures, bricks indicates centralized authority.
- Possibly ruled by merchants or collective governance.
- Social & Economic Life

- Class distinction visible: citadel vs. lower town, rich vs. poor burials.
- Use of ornaments, seals, luxury goods.
- Agriculture + craft + trade = strong economy.
- Craft Specialization
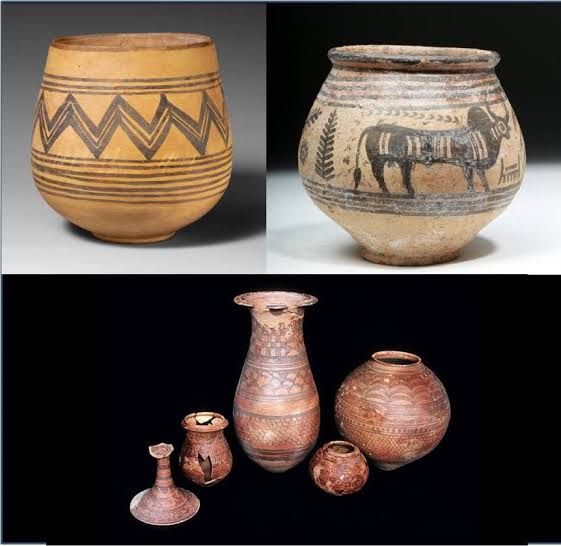

- Evidence of full-time specialists: bead makers, potters, weavers, metal workers.
- Standardization in production shows organized industry.
- Presence of workshops (Lothal, Chanhudaro).
Extra Important Points
- Time Period: 2600 BCE – 1900 BCE (Mature Harappan Phase).
- Major Sites:
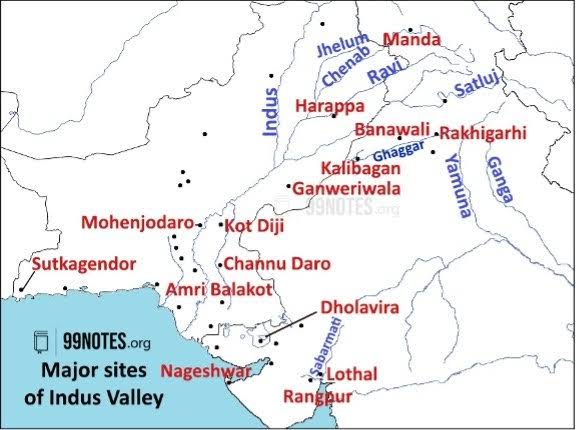
- Harappa (Punjab, Pakistan), Mohenjodaro (Sindh), Dholavira (Gujarat), Lothal (Gujarat), Kalibangan (Rajasthan), Rakhigarhi (Haryana), Banawali.
- Dockyard:

- Lothal (important for trade).
- Metals Used:
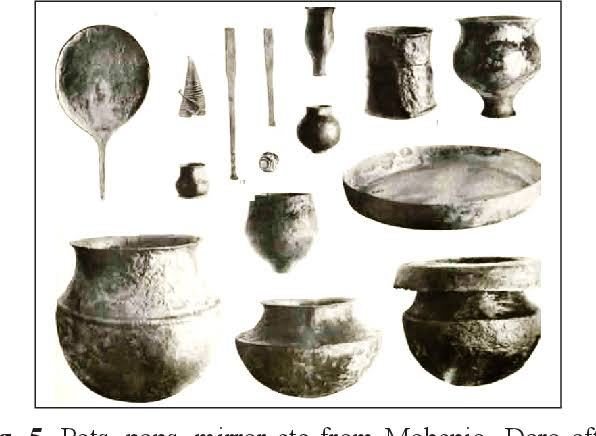

- Copper, bronze, gold, silver (no iron).
- Granaries:

- Found at Harappa and Mohenjodaro.
- Weights & Measures:
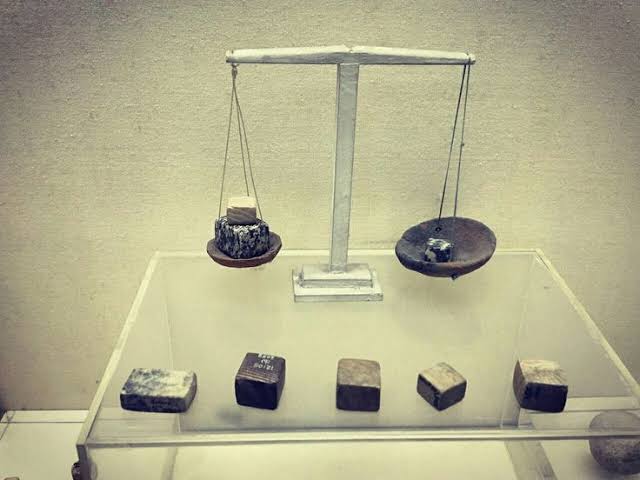

- Cubical weights (binary system).
- Burial Practices:
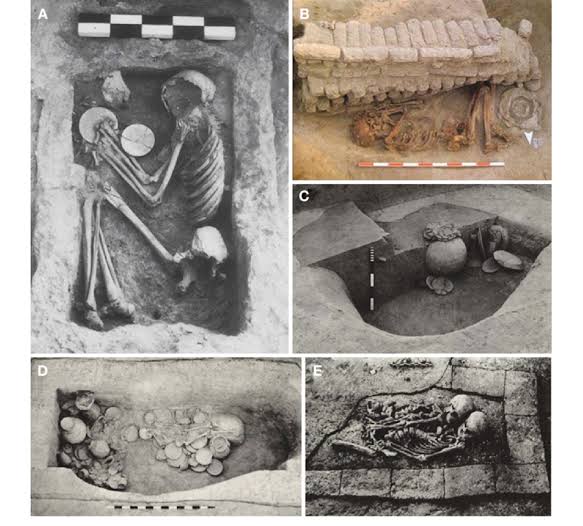
- Pit burials, use of pottery, ornaments in graves.
- Art:
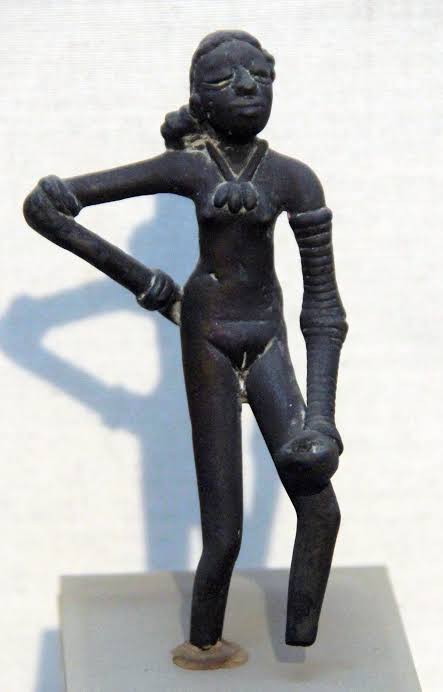

- Terracotta figurines, bronze dancing girl (Mohenjodaro), bearded priest (steatite).
- Engineering Skills:
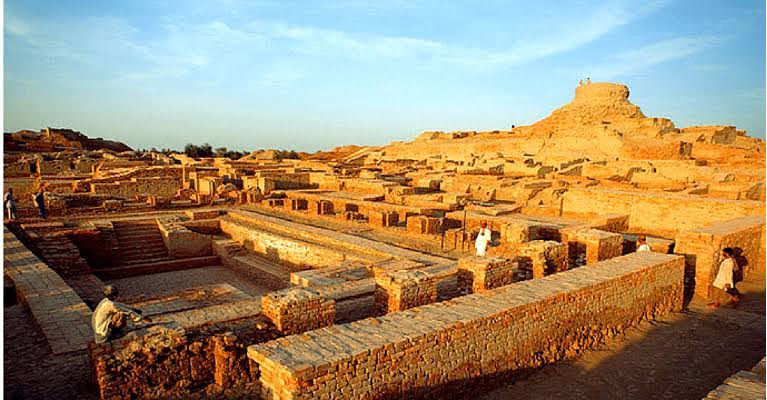

- Great Bath (Mohenjodaro), water management in Dholavira.
📘 Combined Set of 64 MCQs
- Which type of economy existed in the Harappan Civilization?
A) Hunting economy
B) Pastoral economy
C) Agricultural economy
D) Industrial economy
Answer: C) Agricultural economy - Which type of crops were mainly cultivated by the Harappans?
A) Rice and millet
B) Cotton and barley
C) Wheat and barley
D) Tea and coffee
Answer: C) Wheat and barley - Which was the most important cereal crop of the Harappans?
A) Rice
B) Wheat
C) Maize
D) Barley
Answer: D) Barley - Which Harappan site provides the earliest evidence of cotton?
A) Kalibangan
B) Lothal
C) Mohenjodaro
D) Mehrgarh
Answer: D) Mehrgarh - Which animal was most commonly domesticated by the Harappans?
A) Elephant
B) Dog
C) Humped bull
D) Sheep
Answer: C) Humped bull - At which Harappan site is evidence of a ploughed field found?
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Harappa
C) Lothal
D) Kalibangan
Answer: D) Kalibangan - At which Harappan site was a dockyard discovered?
A) Lothal
B) Kalibangan
C) Harappa
D) Mohenjodaro
Answer: A) Lothal - The Harappans had trade relations with which contemporary civilization?
A) Roman Civilization
B) Mesopotamian Civilization
C) Egyptian Civilization
D) Chinese Civilization
Answer: B) Mesopotamian Civilization - What was the main occupation of the Harappan people?
A) Agriculture
B) Hunting
C) Fishing
D) Trading
Answer: A) Agriculture - Which material was mostly used by Harappans for making tools and weapons?
A) Iron
B) Bronze
C) Steel
D) Copper
Answer: B) Bronze - The Harappan Civilization is also called:
A) Vedic Civilization
B) Chalcolithic Civilization
C) Bronze Age Civilization
D) Iron Age Civilization
Answer: C) Bronze Age Civilization - Which Harappan site provides evidence of bead-making industry?
A) Harappa
B) Chanhudaro
C) Lothal
D) Mohenjodaro
Answer: B) Chanhudaro - Which Harappan site is famous for its fire altars?
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Harappa
C) Kalibangan
D) Dholavira
Answer: C) Kalibangan - Which metal was not known to the Harappans?
A) Copper
B) Bronze
C) Tin
D) Iron
Answer: D) Iron - What was the script of Harappans?
A) Pictographic script
B) Brahmi script
C) Kharosthi script
D) Devanagari script
Answer: A) Pictographic script - How many signs were there in the Harappan script?
A) 400–600
B) 700–800
C) 100–200
D) 50–100
Answer: A) 400–600 - Which script is still undeciphered?
A) Harappan script
B) Brahmi script
C) Kharosthi script
D) Greek script
Answer: A) Harappan script - Which was the largest building discovered in Mohenjodaro?
A) Great Bath
B) Granary
C) Assembly Hall
D) Dockyard
Answer: B) Granary - Which unique structure was found at Mohenjodaro?
A) Fire altar
B) Great Bath
C) Dockyard
D) Stadium
Answer: B) Great Bath - The Great Bath was mainly used for:
A) Bathing of kings
B) Community bathing rituals
C) Storage of water
D) Irrigation purpose
Answer: B) Community bathing rituals - Which Harappan city was divided into citadel and lower town?
A) Harappa
B) Mohenjodaro
C) Dholavira
D) All of these
Answer: D) All of these - What was the main building material used by Harappans?
A) Stone
B) Mud brick
C) Burnt brick
D) Timber
Answer: C) Burnt brick - What kind of town planning was found in Harappan Civilization?
A) Circular planning
B) Grid system
C) Irregular planning
D) Cluster system
Answer: B) Grid system - Which Harappan site is famous for water reservoirs?
A) Dholavira
B) Harappa
C) Mohenjodaro
D) Chanhudaro
Answer: A) Dholavira - What was the length and breadth of the largest water reservoir in Dholavira?
A) 79m × 22m
B) 40m × 15m
C) 50m × 20m
D) 60m × 25m
Answer: A) 79m × 22m - The largest Harappan site discovered in India is:
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Harappa
C) Rakhigarhi
D) Dholavira
Answer: C) Rakhigarhi - In which state is Rakhigarhi located?
A) Gujarat
B) Punjab
C) Haryana
D) Rajasthan
Answer: C) Haryana - The first Harappan site discovered was:
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Harappa
C) Rakhigarhi
D) Dholavira
Answer: B) Harappa - Who first discovered Harappa in 1921?
A) Dayaram Sahni
B) Rakhaldas Banerjee
C) John Marshall
D) Mortimer Wheeler
Answer: A) Dayaram Sahni - Who discovered Mohenjodaro in 1922?
A) Dayaram Sahni
B) Rakhaldas Banerjee
C) John Marshall
D) Mortimer Wheeler
Answer: B) Rakhaldas Banerjee - The most common craft in Harappan Civilization was:
A) Bead-making
B) Pottery
C) Metalwork
D) Weaving
Answer: B) Pottery - Harappan pottery was mainly:
A) Red ware with black designs
B) Black ware with red designs
C) Painted grey ware
D) Polished black ware
Answer: A) Red ware with black designs - What is the most important artistic achievement of Harappan Civilization?
A) Bronze dancing girl
B) Stone temples
C) Rock paintings
D) Caves
Answer: A) Bronze dancing girl - The bronze dancing girl statue was found at:
A) Harappa
B) Lothal
C) Mohenjodaro
D) Kalibangan
Answer: C) Mohenjodaro - The bearded priest statue was found at:
A) Harappa
B) Lothal
C) Mohenjodaro
D) Kalibangan
Answer: C) Mohenjodaro - Which game similar to modern chess was played by Harappans?
A) Chaupar
B) Dice game
C) Chess-like board game
D) Ludo
Answer: C) Chess-like board game - Which sport evidence is found in Harappan Civilization?
A) Hunting
B) Bull fighting
C) Horse racing
D) Polo
Answer: B) Bull fighting - Which type of burial practice was followed by Harappans?
A) Cremation
B) Extended burial
C) Tree burial
D) Sky burial
Answer: B) Extended burial - Which animal was not known to Harappans?
A) Horse
B) Dog
C) Bull
D) Elephant
Answer: A) Horse - Which tree was considered sacred by Harappans?
A) Banyan
B) Pipal
C) Neem
D) Mango
Answer: B) Pipal - Which goddess was worshipped by Harappans?
A) Goddess Kali
B) Goddess of Mother Earth
C) Saraswati
D) Durga
Answer: B) Goddess of Mother Earth - Which deity is shown on Harappan seals?
A) Pashupati (Proto-Shiva)
B) Vishnu
C) Indra
D) Varuna
Answer: A) Pashupati (Proto-Shiva) - Which was the main animal depicted on Harappan seals?
A) Horse
B) Unicorn
C) Lion
D) Dog
Answer: B) Unicorn - Which metal was most widely used for Harappan seals?
A) Copper
B) Bronze
C) Steatite
D) Iron
Answer: C) Steatite - The script of Harappans was written from:
A) Left to right
B) Right to left
C) Both directions (Boustrophedon)
D) Top to bottom
Answer: C) Both directions (Boustrophedon) - What was the political system of Harappans?
A) Kingship
B) Republic
C) Democratic
D) None certain
Answer: D) None certain - Which symbol of authority is not found in Harappan Civilization?
A) Palace
B) Statue of king
C) Royal tombs
D) All of these
Answer: D) All of these - The Harappan Civilization belongs to which age?
A) Chalcolithic
B) Neolithic
C) Bronze Age
D) Iron Age
Answer: C) Bronze Age - What was the main reason for decline of Harappan Civilization?
A) Invasion
B) Floods
C) Drought
D) Multiple causes
Answer: D) Multiple causes - Who believed Aryan invasion caused the decline of Harappan Civilization?
A) Mortimer Wheeler
B) Rakhaldas Banerjee
C) Daya Ram Sahni
D) John Marshall
Answer: A) Mortimer Wheeler - Which Harappan site shows evidence of flooding?
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Harappa
C) Kalibangan
D) Lothal
Answer: A) Mohenjodaro - Which site gives evidence of earthquake?
A) Harappa
B) Mohenjodaro
C) Kalibangan
D) Lothal
Answer: C) Kalibangan - Which was the main reason for decline according to modern scholars?
A) Climate change and ecological factors
B) Aryan invasion
C) Foreign attack
D) Drought only
Answer: A) Climate change and ecological factors - The Harappan Civilization flourished between:
A) 1500–500 BCE
B) 3300–1300 BCE
C) 2500–1750 BCE
D) 1000–500 BCE
Answer: C) 2500–1750 BCE - What was the social structure of Harappans?
A) Caste-based society
B) Equalitarian society
C) Slave-based society
D) Kingship-based society
Answer: B) Equalitarian society - Which Harappan site is in Rajasthan?
A) Rakhigarhi
B) Dholavira
C) Kalibangan
D) Mohenjodaro
Answer: C) Kalibangan - Which Harappan site is in Gujarat?
A) Lothal
B) Kalibangan
C) Harappa
D) Rakhigarhi
Answer: A) Lothal - Which Harappan site is in Sindh, Pakistan?
A) Harappa
B) Mohenjodaro
C) Dholavira
D) Lothal
Answer: B) Mohenjodaro - Which Harappan site is in Punjab, Pakistan?
A) Mohenjodaro
B) Lothal
C) Harappa
D) Rakhigarhi
Answer: C) Harappa - Which Harappan site is famous for rice husks?
A) Lothal
B) Harappa
C) Kalibangan
D) Rakhigarhi
Answer: B) Harappa - Which Harappan site is famous for a terracotta plough model?
A) Banawali
B) Mohenjodaro
C) Kalibangan
D) Harappa
Answer: A) Banawali - Which Harappan site is famous for shell bangles and ivory objects?
A) Harappa
B) Lothal
C) Mohenjodaro
D) Chanhudaro
Answer: D) Chanhudaro - Which Harappan site is famous for fire altars and bones of camels?
A) Kalibangan
B) Mohenjodaro
C) Harappa
D) Dholavira
Answer: A) Kalibangan - Which Harappan site is famous for 16 water reservoirs?
A) Rakhigarhi
B) Dholavira
C) Kalibangan
D) Mohenjodaro
Answer: B) Dholavira
📘 Harappan Civilization – Important Questions and Answers
Question 1. Describe the main features of the town planning of the Harappan Civilization.
Answer – Harappan Civilization is famous for town planning. Its main points are as follows –
Planned cities – The cities were divided into two parts –
Upper Citadel – where there were important buildings, warehouses, bathhouses.
Lower Town – where common citizens lived.
Road system –
The roads were straight and cut each other at right angles.
The main roads were wide (up to 9-10 meters).
Drainage system –
Cemented drains came out of every house.
The drains were covered and manholes were made for cleaning at regular intervals.
Construction material –
Bricks were standardized (length-width ratio 4:2:1).
Burned bricks were used extensively.
➡️ This proves that Harappan city planning was of a very advanced and modern level.
Question 2. Describe the drainage system of the Harappan civilization.
Answer –
Organized drains – Drains coming out of each house were connected to the main drains.
Covered drains – They were covered with stone slabs.
Sanitation system – Open spaces and manholes were made in the drains for cleaning.
Water control – Bathrooms were built in the houses from which dirty water went into the drains.
➡️ It is considered to be one of the most advanced drainage systems in the world.
Question 3. Describe the various ways of obtaining raw material for craft production by the inhabitants of the Harappan civilization.
Answer –
Local sources –
Copper from Balochistan.
Copper and semi-precious stones from Rajasthan.
Shells, pearls from Gujarat.
Foreign trade –
Lapis lazuli from Afghanistan.
Copper from Oman.
Gold, silver and other metals from Mesopotamia.
Internal exchange – Grains, animal products were taken from the villages and tools and clothes were given in exchange.
➡️ This shows that the Harappans were dependent on both natural resources and trade relations.
Question 4. Explain the characteristics of the script of Harappan civilization.
Answer –
Pictographic – The signs were mainly in picture form.
Number of signs – About 400–600 signs were used.
Direction of writing – Right to left and sometimes both directions (Boustrophedon).
Unread till now – This script has not been fully read till now.
➡️ This script was used in administration and religious activities.
Question 5. Describe the reasons for the decline of Harappan civilization.
Answer –
Natural disasters – floods, earthquakes etc.
Climate change – changing the course of rivers, drought.
Foreign invasion – opinion of Aryan invasion (by Mortimer Wheeler).
Economic reasons – decline in trade, lack of resources.
➡️ According to modern scholars, its decline was multi-causal.
Question 6. What do you know about Cunningham and John Marshall?
Answer –
Alexander Cunningham –
First Director General of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
He obtained ancient objects from the Harappa site for the first time.
John Marshall –
Officially announced the discovery of Harappa and Mohenjodaro in 1924.
Systematic excavations were carried out under his leadership.
➡️ Both scholars made significant contributions in bringing the Harappan civilization to the world.
Question 7. Describe the methods of subsistence (food) of the Harappan residents.
Answer –
Agriculture – Cultivation of wheat, barley, millet, cotton, rice.
Animal husbandry – Bulls, sheep, goats, dogs, elephants were reared.
Fish and meat – part of the diet.
Grain storage – Large granaries were built.
➡️ Food was varied and balanced.
Question 8. Describe the relations of the Harappan residents with the world.
Answer –
Trade with Mesopotamia – “Meluhha” (Harappa) is mentioned on the seals there.
From Afghanistan – Lapis lazuli.
From Oman – Copper.
Local trade – Textiles, pottery, metal objects.
➡️ Harappa was involved in worldwide trade.
Question 9. How are the seals helpful in giving information about the religious beliefs of the Harappans?
Answer –
Pashupati seal – Presence of the original form of Shiva.
Animal symbols – Unicorn, bull, elephant etc. – Totemism.
Mother Goddess – Worship of fertility.
Sacred tree – Symbol of Peepal tree.
➡️ Seals provide evidence of religious beliefs and gods and goddesses.
Question 10. “There are signs of taking complex decisions and implementing them in Harappan society”, explain this statement and describe the arguments given for central power there.
Answer –
City planning – Settling cities in a planned manner.
Standardization – Same size of bricks, uniform weight and measurement.
Trade control – Long distance trade is not possible without a central organization.
Public buildings – Construction of bathhouse, granary.
➡️ This shows that there was definitely some central power or organized administration.
Question 11. How has the social and economic life of the people of Harappa been described by archaeologists?
Answer –
Social life –
Based on equality.
Contribution of both men and women.
Worship of Mother Goddess and Pashupati in religion.
Economic life –
Agriculture and animal husbandry are the main ones.
Metal crafts, pottery, bead making.
International trade with Mesopotamia.
➡️ Social and economic life was organized and prosperous.
Question 12. How was craft production done in Harappa?
Answer – Craft production in Harappa
Pottery, toys, tablets and statues were also made.
Chanhudaro – main centre of craft production.
Carnelian, jasper, quartz used for making beads.
Metal art – tools and jewellery made from copper, bronze, gold, silver.
Jewellery made from conch shells – Nageshwar and Balakot.







