100 important MCQs Class 11 History Chapter 5 – “Changing Cultural Traditions”
Set 1 – Basic Understanding
Q1. The Renaissance began in which country?
(a) France
(b) England
(c) Italy
(d) Spain
Ans. (c)
Explanation: The Renaissance started in Italy due to its wealthy city-states, trade, and classical heritage.
Q2. The term Renaissance literally means:
(a) Revolution
(b) Rebirth
(c) Enlightenment
(d) Discovery
Ans. (b)
Explanation: “Renaissance” literally means rebirth, referring to the revival of classical learning and culture.
Q3. Which Italian city is considered the cradle of the Renaissance?
(a) Venice
(b) Florence
(c) Rome
(d) Milan
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Florence was a center of art, culture, and humanist thought, patronized by the Medici family.
Q4. Who is known as the “Father of Humanism”?
(a) Petrarch
(b) Dante
(c) Erasmus
(d) Machiavelli
Ans. (a)

Explanation: Petrarch emphasized the study of classical texts and human values, inspiring Renaissance humanism.
Q5. The invention of the printing press is credited to:
(a) Galileo
(b) Gutenberg
(c) Copernicus
(d) Bacon
Ans. (b)

Explanation: Gutenberg invented the printing press (~1450), revolutionizing knowledge dissemination.
Q6. Renaissance thinkers emphasized:
(a) Superstition
(b) Blind faith
(c) Reason and individualism
(d) Church authority
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Humanists promoted rational thinking, individual potential, and secular learning.
Q7. Leonardo da Vinci painted which famous artwork?
(a) The Birth of Venus
(b) The Last Supper
(c) The School of Athens
(d) The Creation of Adam
Ans. (b)

Explanation: Painted in Milan, it depicts human emotion and perspective.
Q8. Michelangelo painted the ceiling of:
(a) Florence Cathedral
(b) St. Peter’s Basilica
(c) Sistine Chapel
(d) St. Paul’s Cathedral
Ans. (c)

Explanation: The Sistine Chapel ceiling shows biblical stories with realistic human anatomy.
Q9. The “Divine Comedy” was written by:
(a) Petrarch
(b) Dante Alighieri
(c) Chaucer
(d) Boccaccio
Ans. (b)

Explanation: Dante’s epic poem depicts the journey through Hell, Purgatory, and Paradise.
Q10. Humanism focused on:
(a) Study of divine laws
(b) Study of human life and achievements
(c) Medieval scholasticism
(d) Religious dogma
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Humanists studied classical literature, philosophy, and human potential.
Q11. Who painted Mona Lisa?
(a) Raphael
(b) Michelangelo
(c) Leonardo da Vinci
(d) Botticelli
Ans. (c)

Explanation: Leonardo combined realism, perspective, and sfumato technique.
Q12. The Renaissance period roughly spanned from:
(a) 12th to 14th century
(b) 14th to 17th century
(c) 16th to 18th century
(d) 10th to 12th century
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The Renaissance began in the 1300s and lasted till the 1600s.
Q13. Which classical civilizations inspired Renaissance scholars?
(a) Chinese and Indian
(b) Roman and Greek
(c) Persian and Egyptian
(d) Babylonian and Mesopotamian
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Greek and Roman texts were rediscovered, influencing art, architecture, and philosophy.
Q14. Who wrote The Prince, a guide for rulers?

(a) Petrarch
(b) Machiavelli
(c) Erasmus
(d) Luther
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The book provided practical advice on statecraft, power, and governance.
Q15. The term “Renaissance Man” refers to:
(a) A wealthy merchant
(b) A scholar skilled in many fields
(c) A religious reformer
(d) A scientist
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Renaissance men were versatile, excelling in arts, science, and literature.
Q16. The Protestant Reformation was started by:

(a) Martin Luther
(b) Calvin
(c) Zwingli
(d) Henry VIII
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Luther’s 95 Theses criticized Church corruption, starting the Reformation.
Q17. The ‘Age of Exploration’ was inspired by Renaissance ideas of:
(a) Adventure and discovery
(b) Fear and isolation
(c) Religion only
(d) Agricultural development
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Curiosity, humanism, and knowledge of geography encouraged exploration.
Q18. Renaissance art mainly emphasized:
(a) Religious themes only
(b) Human emotions and realism
(c) Abstract shapes
(d) Monastic life
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Artists used anatomy, perspective, and naturalism to depict reality.
Q19. Which invention helped spread Renaissance ideas quickly?
(a) Compass
(b) Telescope
(c) Printing press
(d) Steam engine
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Allowed mass production of books, increasing literacy and knowledge.
Q20. Who painted The School of Athens?
(a) Raphael
(b) Michelangelo
(c) Botticelli
(d) Giotto
Ans. (a)

Explanation: Depicts philosophers, emphasizes reason, knowledge, and classical ideals.
Q21. “Utopia” was written by:

(a) Thomas More
(b) Erasmus
(c) Bacon
(d) Petrarch
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Imaginary perfect society exploring humanist ideals.
Q22. The Renaissance encouraged the study of:
(a) The Bible only
(b) Humanities – literature, philosophy, and art
(c) Warfare
(d) Monastic rules
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Focused on secular education and human potential.
Q23. The Medici family was famous for being:
(a) Artists
(b) Religious leaders
(c) Patrons of art and learning
(d) Explorers
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Supported artists, architects, and humanist scholars in Florence.
Q24. The term secularism refers to:
(a) Worship of nature
(b) Separation of religion from worldly life
(c) Obedience to the Church
(d) Devotion to priests
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Renaissance emphasized worldly life alongside religious faith.
Q25. Renaissance art first developed perspective (depth) through:
(a) Frescoes
(b) Geometrical drawing
(c) Linear perspective
(d) Gothic design
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Artists like Brunelleschi used geometric techniques to create depth.
Set 2 – Conceptual & Chronological
Q26. The Renaissance began in Italy mainly due to:
(a) Isolation from the Church
(b) Wealthy city-states and trade
(c) Decline of education
(d) Monastic revival
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Italian cities like Florence and Venice were wealthy due to trade. This wealth funded art, education, and humanist studies.
Q27. Which movement questioned the authority of the Catholic Church?
(a) Renaissance
(b) Reformation
(c) Industrial Revolution
(d) Enlightenment
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The Reformation challenged Church corruption, indulgences, and authority.
Q28. The focus on classical literature is called:
(a) Humanism
(b) Rationalism
(c) Classicism
(d) Nationalism
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Scholars revived Greek and Roman literature, emphasizing classical knowledge.
Q29. Who among the following was both a scientist and artist?
(a) Petrarch
(b) Leonardo da Vinci
(c) Raphael
(d) Erasmus
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Leonardo was a polymath – painter, sculptor, engineer, and anatomist.
Q30. Who developed the heliocentric theory?
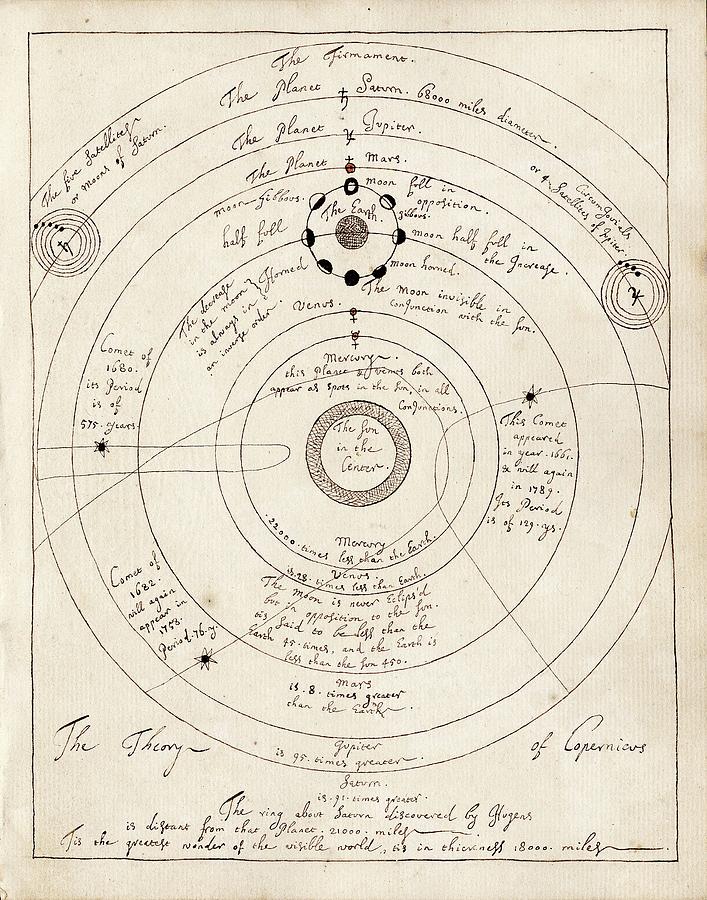
(a) Copernicus
(b) Galileo
(c) Newton
(d) Kepler
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Copernicus proposed that the Sun, not Earth, is the center of the universe.
Q31. Galileo’s telescope confirmed:

(a) The Earth is flat
(b) The Sun revolves around Earth
(c) The Earth revolves around the Sun
(d) The stars are stationary
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Galileo observed moons of Jupiter and phases of Venus, supporting heliocentrism.
Q32. The Printing Revolution began in:
(a) 1439
(b) 1450
(c) 1475
(d) 1500
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Gutenberg’s movable-type printing press (~1450) allowed mass book production.
Q33. Martin Luther’s 95 Theses were posted in:
(a) Rome
(b) Wittenberg
(c) Paris
(d) London
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Luther challenged indulgences and Church corruption in 1517.
Q34. Erasmus wrote:
(a) Praise of Folly
(b) Utopia
(c) The Prince
(d) The Republic
Ans. (a)

Explanation: Erasmus satirized Church corruption and promoted humanist ideals.
Q35. Who was the English playwright known as “The Bard of Avon”?
(a) Chaucer
(b) Shakespeare
(c) Bacon
(d) Milton
Ans. (b)

Explanation: Shakespeare was a key literary figure of the Renaissance in England.
Q36. Which explorer’s voyages linked Europe with Asia and the Americas?
(a) Vasco da Gama
(b) Columbus
(c) Magellan
(d) All of these
Ans. (d)
Explanation: Explorers like Columbus, Magellan, and Vasco da Gama connected continents through trade and navigation.
Q37. The Renaissance spread from Italy to:
(a) France → Spain → England
(b) England → Italy → France
(c) Spain → Italy → France
(d) Greece → Egypt → Rome
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Italian ideas, art, and humanism spread north via trade, scholars, and printing.
Q38. The Scientific Revolution was a direct result of:
(a) Feudalism
(b) Renaissance humanism and curiosity
(c) Church decrees
(d) Religious warfare
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Humanists encouraged observation, questioning, and empirical study, leading to science.
Q39. The study of anatomy and nature in Renaissance art shows:
(a) Idealism
(b) Realism
(c) Romanticism
(d) Abstract art
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Artists like Leonardo studied the human body to depict accurate anatomy.
Q40. The artist who designed the dome of St. Peter’s Basilica was:

(a) Michelangelo
(b) Bramante
(c) Raphael
(d) Giotto
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Michelangelo’s architectural design combined classical forms with innovative engineering.
Q41. Which century is considered the height of Renaissance art?
(a) 13th
(b) 14th
(c) 15th
(d) 16th
Ans. (d)
Explanation: The 1500s saw masterpieces from Leonardo, Michelangelo, Raphael, and Titian.
Q42. The Reformation led to the rise of:
(a) New Catholic Churches
(b) Protestant Churches
(c) Pagan rituals
(d) Islamic expansion
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Reformers like Luther and Calvin established new Christian denominations.
Q43. The Council of Trent was held to:
(a) Expand Catholicism
(b) Reform the Catholic Church
(c) Punish reformers
(d) Ban humanism
Ans. (b)
Explanation: 1545–1563, the council clarified doctrines and addressed corruption.
Q44. “The Birth of Venus” was painted by:

(a) Botticelli
(b) Raphael
(c) Michelangelo
(d) Leonardo
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Botticelli used mythological themes, elegance, and idealized beauty.
Q45. The Renaissance encouraged a spirit of:
(a) Inquiry and experimentation
(b) Blind obedience
(c) Isolation
(d) Dogma
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Humanists promoted learning, exploration, and independent thought.
Q46. The artist Raphael is known for his:
(a) Sculptures
(b) Frescoes
(c) Dome structures
(d) Scientific works
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Raphael’s frescoes like The School of Athens display perspective and classical ideals.
Q47. Renaissance thinkers believed that man was:
(a) Helpless
(b) The center of the universe
(c) Dependent on the Church
(d) Bound by destiny
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Humanists emphasized human potential and achievements.
Q48. The Age of Reason later grew from:
(a) Renaissance humanism
(b) Industrialization
(c) Crusades
(d) Roman law
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Enlightenment thinkers inherited humanist ideas of rationality and inquiry.
Q49. Renaissance architecture revived:
(a) Gothic style
(b) Greek and Roman columns and domes
(c) Medieval castles
(d) Baroque decorations
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Architects like Brunelleschi and Alberti revived classical forms.
Q50. The Renaissance was closely linked to:
(a) Decline of trade
(b) Rise of urban centers and merchants
(c) Isolation from Europe
(d) Monastic expansion
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Urban wealth and merchant patronage financed art, literature, and science.
Set 3 – Assertion–Reason & Source-Based
Q51. Assertion (A): Renaissance artists used perspective to create depth.
Reason (R): They aimed to make paintings look more realistic.
(a) A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation.
(b) A and R are true, but R is not the explanation.
(c) A is true, R is false.
(d) Both false.
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Perspective allowed artists to create a three-dimensional effect, making art appear realistic.
Q52. Assertion (A): The Church supported every new scientific discovery.
Reason (R): The Church was open to questioning traditional beliefs.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans: (d)
Explanation: The Church often opposed scientific discoveries that contradicted biblical teachings, e.g., Galileo.
Q53. “Man is the measure of all things.” – This statement reflects:
(a) Medievalism
(b) Humanism
(c) Scholasticism
(d) Mysticism
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Humanism emphasized human potential and achievements as central.
Q54. “Give me a place to stand and I will move the Earth.” – This was said by:
(a) Galileo
(b) Archimedes
(c) Copernicus
(d) Newton
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Archimedes described the power of leverage, showing human understanding of natural laws.
Q55. Who among the following was a Renaissance sculptor?
(a) Leonardo
(b) Raphael
(c) Donatello
(d) Giotto
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Donatello was a key sculptor of the Italian Renaissance, famous for realism in sculptures.
Q56. Assertion (A): Printing reduced dependence on the Church.
Reason (R): People could now read the Bible in their own languages.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans: (d)
Explanation: The Church often opposed scientific discoveries that contradicted biblical teachings, e.g., Galileo.
Ans. (a)
Explanation: The printing press allowed vernacular texts, reducing clergy’s monopoly over knowledge.
Q57. Erasmus criticized:
(a) Superstition and Church corruption
(b) Humanism
(c) Science
(d) Classical learning
Ans. (a)
Explanation: In Praise of Folly, Erasmus satirized superstition and clerical abuses.
Q58. Assertion (A): Renaissance thinkers broke away from medieval scholasticism.
Reason (R): They emphasized observation and experience.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Empirical observation replaced dogma; scholars relied on evidence and classical texts.
Q59. The first book printed by Gutenberg was:
(a) Utopia
(b) The Bible
(c) The Prince
(d) Divine Comedy
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Gutenberg’s Bible (~1455) was the first major book printed using movable type.
Q60. Assertion (A): Wealthy patrons encouraged art and culture.
Reason (R): They wanted to display power and prestige.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Patrons like the Medici funded artists to show influence and social status.
Q61. The Renaissance marked a transition from:
(a) Ancient to Modern Age
(b) Modern to Medieval Age
(c) Classical to Feudal Age
(d) None
Ans. (a)
Explanation: The Renaissance bridged the Medieval period and the Modern era with new learning and culture.
Q62. “Heavenly spheres revolve around the Sun.” – Associated with:
(a) Newton
(b) Copernicus
(c) Galileo
(d) Kepler
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Copernicus proposed the heliocentric model, challenging geocentric views.
Q63. The term vernacular literature refers to:
(a) Latin language
(b) Local language of the people
(c) Greek writings
(d) Church hymns
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Literature written in local languages increased literacy and accessibility.
Q64. Assertion (A): Renaissance promoted secularism.
Reason (R): People focused more on worldly achievements.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Renaissance art, literature, and education emphasized non-religious subjects.
Q65. The technique of sfumato was used by:
(a) Raphael
(b) Leonardo da Vinci
(c) Botticelli
(d) Michelangelo
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Sfumato blended colors subtly to achieve realistic shading.
Q66. Source-based: “A man can do all things if he will.” – This quote expresses:
(a) Divine authority
(b) Human potential
(c) Church control
(d) Political power
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Reflects humanist belief in personal ability and free will.
Q67. Assertion (A): Renaissance thinkers rediscovered Greek manuscripts.
Reason (R): They were preserved in Byzantine and Arab libraries.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Classical texts were copied and studied, fueling humanist scholarship.
Q68. The term Renaissance Humanism means:
(a) Belief in supernatural powers
(b) Study of humanity through classical texts
(c) Church-based studies
(d) Astrology
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Humanism emphasized reason, ethics, and education based on classical texts.
Q69. Assertion (A): Scientific methods emphasized observation.
Reason (R): It was believed that knowledge should be tested by reason.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Empirical observation and logic became central to scientific inquiry.
Q70. Which invention revolutionized knowledge distribution?
(a) Telescope
(b) Compass
(c) Printing press
(d) Microscope
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Books could be mass-produced, spreading ideas faster than ever.
Q71. Assertion (A): Renaissance artists depicted the human body realistically.
Reason (R): They studied anatomy and nature.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Artists like Leonardo dissected corpses to understand anatomy for realistic art.
Q72. “The Book of the Courtier” was written by:

(a) Castiglione
(b) Petrarch
(c) Erasmus
(d) Dante
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Castiglione’s book described ideal Renaissance etiquette and humanist education.
Q73. Assertion (A): Florence became a cultural center.
Reason (R): The Medici family were great patrons of art.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (a)
Explanation: The Medici funded art, architecture, and learning, making Florence a hub.
Q74. Assertion (A): The Renaissance was confined to Italy.
Reason (R): Printing and trade did not reach other parts.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans. (d)
Explanation: Renaissance spread to France, England, and the Netherlands via trade, printing, and travel.
Q75. “Art should imitate nature.” – Expresses:
(a) Medieval faith
(b) Renaissance realism
(c) Romanticism
(d) Modernism
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Artists focused on realistic depictions of human figures and nature.
Set 4 – Advanced/Analytical & Mixed Types
Q76. The Renaissance symbolized a shift from:
(a) Faith to reason
(b) Science to religion
(c) Trade to feudalism
(d) Urban to rural life
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Renaissance emphasized rational thinking and human observation over blind faith and medieval dogma.
Q77. The city-state system of Italy promoted:
(a) Rivalry and innovation
(b) Isolation
(c) Agricultural decline
(d) Religious orthodoxy
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Independent city-states like Florence and Venice encouraged competition, wealth accumulation, and innovation in art, science, and politics.
Q78. Match the following artists with their works:
1.Leonardo da Vinci – (a) The School of Athens
2. Michelangelo—- – (b) The Last Supper
3. Raphael – ————(c) Sistine Chapel ceiling
(a) 1-b, 2-c, 3-a
(b) 1-c, 2-a, 3-b
(c) 1-a, 2-b, 3-c
(d) 1-b, 2-a, 3-c
Ans. (a)
Explanation:
Leonardo da Vinci: The Last Supper
Michelangelo: Sistine Chapel ceiling
Raphael: The School of Athens
Q79. “Human beings have free will and dignity.” This idea belongs to:
(a) Humanism
(b) Scholasticism
(c) Feudalism
(d) Theocracy
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Renaissance humanism emphasized human dignity, potential, and moral responsibility.
Q80. Renaissance art introduced:
(a) Flat images
(b) Depth and proportion
(c) Symbolic patterns only
(d) Religious rigidity
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Techniques like linear perspective, sfumato, and chiaroscuro created depth and realism.
Q81. Which Renaissance scientist improved the telescope?
(a) Copernicus
(b) Galileo
(c) Kepler
(d) Bacon
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Techniques like linear perspective, sfumato, and chiaroscuro created depth and realism.
Q82. The spirit of the Renaissance can best be summed up as:
(a) Questioning and creativity
(b) Faith and superstition
(c) Obedience and fear
(d) Silence and obedience
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Emphasis was on curiosity, experimentation, and exploration in arts, science, and philosophy.
Q83. Match the following:
A. Gutenberg – (i) Printing
B. Copernicus – (ii) Heliocentrism
C. Machiavelli – (iii) Politics
(a) A-i, B-ii, C-iii
(b) A-ii, B-iii, C-i
(c) A-iii, B-i, C-ii
(d) A-i, B-iii, C-ii
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Gutenberg: printing press; Copernicus: heliocentric theory; Machiavelli: The Prince on politics.
Q84. The Renaissance broke the monopoly of:
(a) Monarchs
(b) The Church over knowledge
(c) Guilds
(d) Nobility
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Printing and humanist scholarship reduced Church control over education and knowledge.
Q85. The idea of questioning authority emerged during:
(a) Renaissance
(b) Crusades
(c) Feudal period
(d) Dark Age
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Humanist education and observation encouraged critical thinking and challenging tradition.
Q86. The development of perspective is linked with:
(a) Architecture
(b) Painting
(c) Sculpture
(d) Literature
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Artists like Brunelleschi and Masaccio developed linear perspective for realistic paintings.
Q87. The Renaissance influenced political thought by:
(a) Promoting divine kingship
(b) Encouraging secular statecraft
(c) Supporting Church rule
(d) Banning political debates
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Machiavelli emphasized pragmatic, secular politics rather than religious guidance.
Q88. The Mona Lisa is displayed in:
(a) Uffizi Gallery
(b) Louvre Museum
(c) Vatican Museum
(d) National Gallery
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Leonardo da Vinci’s Mona Lisa is housed in the Louvre, Paris, and exemplifies Renaissance realism.
Q89. “Reason is the guide to truth.” This belief reflects:
(a) Humanism
(b) Rationalism
(c) Romanticism
(d) Mysticism
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Renaissance thinkers relied on logic and observation to understand the natural world.
Q90. Renaissance education promoted:
(a) Memorization
(b) Critical thinking
(c) Dogmatic learning
(d) Religious rituals
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Schools emphasized study of humanities, critical thinking, and ethical reasoning.
Q91. The Renaissance replaced feudal society with:
(a) Urban merchant society
(b) Tribal systems
(c) Monastic life
(d) Rural serfdom
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Cities and trade centers allowed rise of a wealthy, educated merchant class.
Q92. The Renaissance encouraged exploration mainly due to:
(a) Scientific
(b) Religious faith
(c) Feudal obligations
(d) Agricultural expansion
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Knowledge of astronomy, geography, and curiosity motivated voyages by explorers like Columbus and da Gama.
Q93. Which invention improved literacy and learning during Renaissance?
(a) Compass
(b) Printing press
(c) Telescope
(d) Astrolabe
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Printing allowed mass production of books, spreading literacy and classical knowledge.
Q94. Renaissance artists were inspired by:
(a) Medieval scholasticism
(b) Classical Greek and Roman art
(c) Islamic architecture
(d) Egyptian pyramids
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Classical ideals of proportion, beauty, and harmony were revived in art.
Q95. The Reformation influenced the Renaissance by:
(a) Strengthening Church monopoly
(b) Encouraging critical thinking and literacy
(c) Reducing trade
(d) Promoting serfdom
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Protestant Reformation encouraged reading of scripture, education, and questioning authority.
Q96. Which thinker wrote The Prince?
(a) Erasmus
(b) Machiavelli
(c) Copernicus
(d) Galileo
Ans: (b)
Explanation: The Prince advised rulers on realpolitik and secular governance.
Q97. Renaissance science relied on:
(a) Faith and scripture
(b) Observation and experimentation
(c) Oral tradition
(d) Alchemy only
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Empirical evidence replaced blind acceptance of authority.
Q98. Renaissance humanists emphasized:
(a) Astrology
(b) Study of classics, literature, and ethics
(c) Witchcraft
(d) Church law
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Classical literature and ethical philosophy were central to humanist education.
Q99. Assertion (A): Renaissance painters studied anatomy for realistic figures.
Reason (R): Understanding muscles and proportions improved art quality.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Artists dissected cadavers to master realistic depiction of the human body.
Q100. Assertion (A): Renaissance ideas spread across Europe.
Reason (R): Printing press, trade, and travel facilitated cultural exchange.
(a) Both A and R are true, R is correct explanation
(b) Both A and R are true, R is not correct explanation
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both false
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Italy was the origin, but ideas quickly reached France, England, and the Netherlands.







