Question 1: Why was trade important to the Mongols?
Answer:
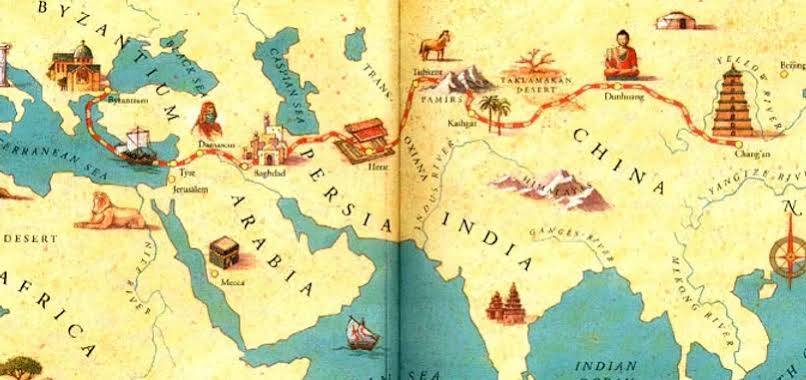
० The Mongols lived in the grasslands where agriculture and resources were scarce, so they had to depend on trade to meet their needs.
० They imported textiles, agricultural equipment, tea, silk, etc. from China and the Islamic world.
० Through trade they strengthened economic relations and ensured the security of international routes (such as the Silk Road).
Question 2: What is the meaning of the term ‘Quriltai’?

Answer:
० The Quriltai was a major assembly of Mongol society in which important decisions were taken.
० It took decisions such as the election of khans (rulers), planning of wars and distribution of loot.
० It was a traditional institution that was central to the political organisation of the Mongols.
Question 3: Describe two major sources about the Mongol Empire.
Answer:
‘० The Secret History of the Mongols’ – It gives an insider’s view of the Mongols and depicts the life of Genghis Khan in detail.
० Marco Polo’s Travelogue – It gives an account of Mongol rule, trade and administration from a European perspective.
० Persian historians such as Rashid al-Din and al-Juwaini have given detailed information on Mongol campaigns and society.
Question 4: Who was Batu? Write three things about him.

Answer:
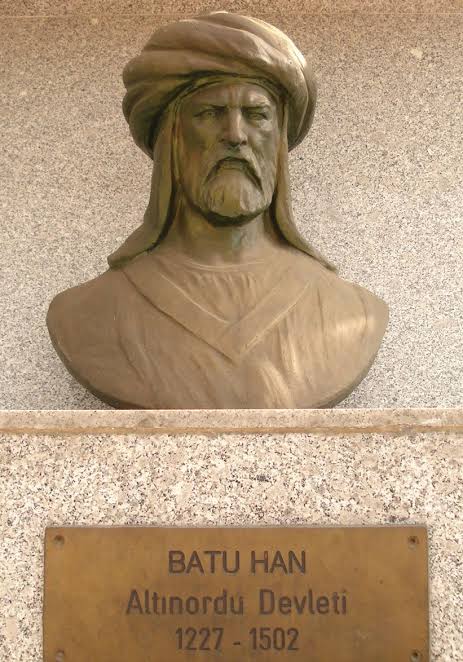
० Batu was the grandson of Genghis Khan and son of Jochi.
० He led Mongol armies and conducted devastating campaigns to Russia, Poland and Hungary.
० Batu established a sub-empire called the “Golden Horde” in the region of Russia.
Question 5: Describe the political and military system during the reign of Genghis Khan.
Answer:
० Genghis Khan transformed Mongol society into an organised system based on military discipline.
० The army was divided into units (Tumen) of ten thousand each, led by able officers.
० A ‘servant’ system based on loyalty was promoted, in which fiefs were given in exchange for service.
० Collective decisions were taken through the Kuriltai, which elected new Khans.
० Genghis Khan divided the empire’s territories among his four sons – Jochi, Chagatai, Ogedai and Tolui.
० He promoted religious tolerance and appointed administrative experts.
० The ‘Yam’ system (horse-borne postal service) was established for communication.
० Discipline, swiftness and strategy in war made the Mongol army invincible.
Question 6: Explain the causes of conflict between pastoralists and agriculturalists in nomadic societies.
Answer:
० The pastoral society depended on grasslands and pastures for its livelihood while the agricultural society practiced permanent agriculture.
० There was conflict between the two societies over the use of land, especially in the border areas.
० The cattle of the pastoralists often damaged the crops of the farmers, causing tension.
० The efforts of nomadic societies to collect taxes and revenue from the agricultural communities increased the conflict.
० Agrarian empires often built protective walls and forts to prevent the intrusion of nomads.
० Cultural differences such as lifestyle, religion and social organization also became causes of conflict.
० Conflict increased due to the limitation of water and food resources.
० Sometimes these conflicts turned into large military campaigns and looting.
Question 7: What is the significance of the legacy of the Mongol Empire in world history?
Answer:
० The Mongols established stability across Eurasia, allowing trade along the Silk Road to flourish.
० They introduced postal systems, military organization and the legal code ‘Yasa’ which brought administrative stability.
० The Mongols promoted religious tolerance – Muslims, Christians, Buddhists were all respected.
० The exchange of cultural and scientific knowledge accelerated between Asia and Europe.
० The Mongol Empire played a major role in linking Europe and Asia politically and commercially.
० They left lasting effects such as the establishment of the Yuan dynasty in China and the Ilkhan Empire in Persia.
० The organization of their armies and war tactics inspired subsequent empires (such as the Mughals).
० Although the Mongol invasions were devastating, the stability that followed them marked a new turning point in world history.
Question 8: Why were Mongol warriors considered good soldiers?
Answer:
० The Mongols learned horse riding and archery from childhood, making them skilled horsemen and archers.
० Their military training was rigorous and they were prepared to endure harsh weather and hunger and thirst.
० Their tactics of covering long distances on horseback, attacking swiftly and retreating made them unique.
Question 9: What was ‘Yasa’? Why was it important for the Mongol Empire?
Answer:
० Yasa was a code of law adopted by the Mongols and created by Genghis Khan.
० It regulated military discipline, social behaviour and the penal system.
० Yasa helped maintain unity and discipline throughout the empire.
Question 10 : Describe the features of the military tactics of the Mongol army.

Answer:
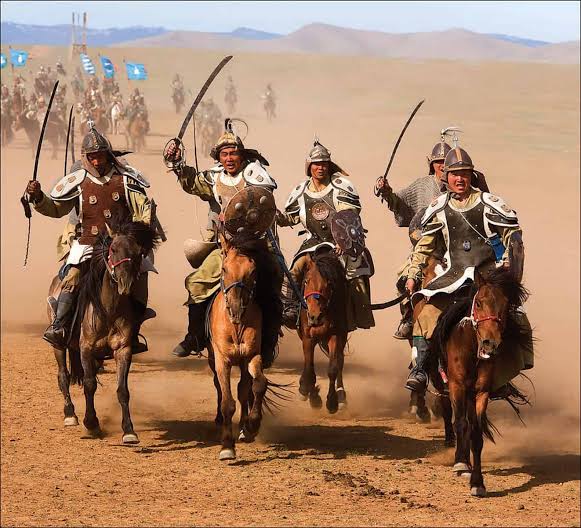
० The Mongol army was divided into decimal systems – groups of ten, hundred, thousand and ten thousand soldiers.
० He adopted surprise tactics like feigned retreat.
० He developed efficient networks (yam) for gathering information, spying and sending messages.
Question 11 : Why is Genghis Khan considered a great military leader?

Answer:
० Genghis Khan unified the Mongol tribes and created an organised military force.
० He adopted decimal military structure which was disciplined and efficient.
० He was an excellent strategist – feigned retreat, encirclement etc.
० He promoted soldiers on the basis of merit, not lineage.
० Genghis Khan enforced a strict system of discipline.
० He introduced laws like Yasa which enforced uniform rules throughout the empire.
० He used to attack his enemies suddenly and swiftly which took opponents by surprise.
० His communication network (yam) enabled him to take quick and effective decisions.
Question 12 : Explain the military system and conquest strategies of the Mongol Empire.
Answer:
० The army was divided into decimal units – 10, 100, 1000, 10,000.
० Responsibility and discipline were strict in every unit.
० The soldiers were given rigorous training – tolerating hunger and thirst, fast horse riding etc.
,० Strategies like fake retreats, sieges, night attacks were adopted.
० An atmosphere of brutality and fear was created to break the morale of the enemy.
० Moving the army from one place to another at a fast speed was their strength.
० Orders reached promptly through an efficient communication system (yam).
० After conquest they enforced strict administration to maintain peace in the empire.







