SECTION – A (MCQs, 1 Mark Each)
Q1. Look at the picture carefully.
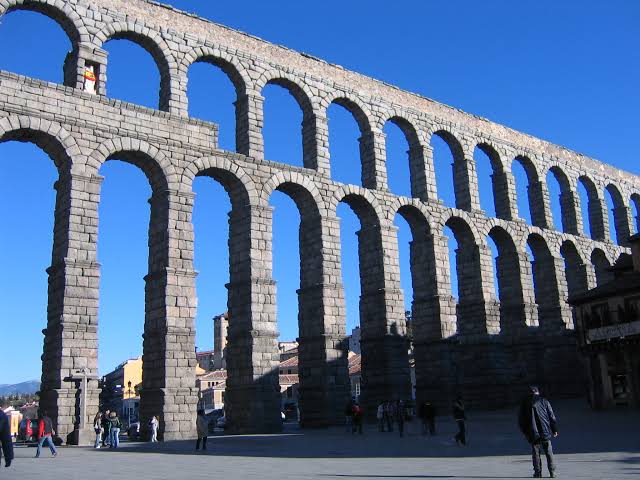

(A) Large Aqueduct
(B) Old Building
(C) Palace of King of Roman empire
(D) Cathedral
✅ Answer: (A) Large Aqueduct
Note (Visually Impaired): Enmerkar was the king of which city of Mesopotamia?
✅ Answer: Uruk
Q2. The name Mesopotamia is derived from which language?
(A) Aramaic
(B) Latin
(C) Akkadian
(D) Greek
✅ Answer: (D) Greek (“meso” = between, “potamos” = rivers).
Q3. Which of the following statements are correct?
Statement I: Archaeology in Mesopotamia began in 1840s.
Statement II: Mesopotamia was not very important to Europeans.
(A) Only I
(B) Only II
(C) Both are correct
(D) Both are incorrect
✅ Answer: (A) Only I
Q4. The Roman Silver Coin, known as Denarius, weighed ___ gm of pure silver.
(A) 2½ gm
(B) 4½ gm
(C) 5½ gm
(D) 3½ gm
✅ Answer: (B) 4½ gm
Q5. Match the following:
I – Roman Emperor | II – Important Events
(i) Augustus | (d) Principate
(ii) Diocletian | (a) Reorganise Empire into 100 provinces
(iii) Constantine | (b) Solidus Coin
(iv) Justinian | (c) Highwater mark of prosperity
Correct Match:
✅ Answer: (B) (i)-d, (ii)-a, (iii)-b, (iv)-c
Q6. Consider the following statements:
Statement I: Ur was excavated in 1930s.
Statement II: Narrow streets show Ur was planned.
Options: (A) Only I (B) Only II (C) Both (D) Neither
✅ Answer: (C) Both are correct
Q7. Who was Temujin’s first friend and trusted companion?
(A) Yesugei
(B) Ong Khan
(C) Jamuqa
(D) Boghurchu
✅ Answer: (D) Boghurchu
Q8. Today Mesopotamia is part of which country?
(A) Iran
(B) Afghanistan
(C) Iraq
(D) China
✅ Answer: (C) Iraq
Q9. Roman Empire got best wine from:
(A) Campania
(B) Sicily
(C) Galilee
(D) Spain
✅ Answer: (A) Campania
Q10. What do you understand by the term Barbarian?
✅ Answer: A Barbarian was a person living outside the Roman Empire, considered uncivilized by the Romans.
Q11. The Secret History of the Mongols and Marco Polo versions differ.
✅ Answer: (A) Both are correct
Q12. Match the following:
(i) Spain – (b) Isabelle & Ferdinand
(ii) England – (c) Henry VII
(iii) France – (d) Louis XI
(iv) Austria – (a) Maximilian
✅ Answer: (B) (i)-b, (ii)-c, (iii)-d, (iv)-a
Q13. The Kings of France were linked to their subjects by:
✅ Answer: (D) Vassalage
Q14. Mesopotamian social system (legal texts):
(i) Joint family was norm.
(ii) Father was head.
(iii) Sons inherited.
✅ Answer: (D) i, ii, iii (All correct)
Q15. Which one is not Post-Roman state?
(A) Visigoths in Spain
(B) Franks in Gaul
(C) Saint Augustine in North Africa
(D) Lombards in Italy
✅ Answer: (C) Saint Augustine in North Africa
Q16. Feudalism developed in England in:
✅ Answer: (D) Eleventh Century
Q17. Assertion (A): Cuneiform sign = syllables.
Reason (R): Scribes learnt hundreds of signs.
✅ Answer: (A) Both correct and R explains A
Q18. Match Genghis Khan’s life:
(i) Original Name – (b) Temujin
(ii) Father – (a) Yesugei
(iii) Blood-brother – (d) Jamuqa
(iv) First Ally – (c) Boghurchu
✅ Answer: (A) (i)-b, (ii)-a, (iii)-d, (iv)-c
Q19. Tithe & Taille:
Statement I: Tithe = church tax.
Statement II: Taille = tax on clergy/nobles.
✅ Answer: (A) Only I
Q20. Groups of monks not based in monastery were called:
✅ Answer: (B) Friars
Q21. Assembly of Mongol Chieftains was:
✅ Answer: (C) Quriltai
SECTION – B (3 Marks Each)
Q22. “Iraq is a country of geographical diversity”. Explain it by giving examples? (3)
- Northern Iraq has fertile plains watered by Tigris & Euphrates.
- Central Iraq has desert regions.
- Southern Iraq has marshes & date palm areas near Persian Gulf.
OR – Write about the Nomadic Communities of Mesopotamian?
- Pastoral nomads lived on herding.
- They moved seasonally between grasslands.
- They supplied wool, meat, and labor to cities.
Q23. Write in brief about the lower class which was collectively known as Humiliores of the Roman Empire? (3).
- They were poor commoners.
- Included small farmers, artisans, and landless laborers.
- They paid heavy taxes and had few political rights.
Q24. What was the legal code of Genghis Khan? (3)
- Set of rules to govern Mongol empire.
- Covered military, civil, and criminal law.
- Ensured strict discipline, loyalty, and justice.
Q25. Explain the Rapid Courier System of Genghis Khan? (3)
- Relay system of mounted messengers (Yam).
- Posts set at fixed distances with fresh horses.
- Allowed quick communication across empire.
Q,26. What is the basis of economic organisation of Europe? Write down its main features? (3).
- Manorial system – agriculture mainstay.
- Serfs worked on lord’s estate.
- Self-sufficient economy with limited trade.
Q27. How Cathedrals were built in Europe? (3)
- Built in Gothic style with pointed arches.
- Large stained-glass windows & tall towers.
- Took decades, involved guild craftsmen.
OR – How did the fourth class of Society came into existence in Europe?
- Merchants, traders, artisans emerged.
- Grew due to revival of towns.
- Became independent from feudal lords.
SECTION – C (8 Marks Each)
Q28. Write in detail about the development of writing in Mesopotamia. (8 Marks)
Answer:
० Legacy: Cuneiform influenced later scripts and marked the beginning of recorded history.
० Origin of Writing: Writing first appeared in Mesopotamia around 3200 BCE in the city of Uruk.
० Purpose: Initially, it was developed for economic transactions like recording taxes, goods, and trade.
० Clay Tablets: Mesopotamians used clay tablets and a reed stylus to press wedge-shaped symbols.
० Cuneiform Script: This wedge-shaped script is called Cuneiform.
० Evolution: At first, pictographs (pictures) were used; later they became abstract signs.
० Wider Use: Writing was then used for royal inscriptions, laws (Code of Hammurabi), literature (Epic of Gilgamesh), and education.
० Schools (Edubbas): Special schools trained scribes, showing the importance of writing in administration.
OR – Discuss the contributions of Mesopotamian civilization.
Answer:
० Cultural Legacy: Influenced later civilizations like Greek and Persian.
० Writing System: Developed cuneiform writing, earliest known script.
० Mathematics & Astronomy: Introduced base-60 system, accurate calendars.
० Architecture: Built ziggurats, temples, and advanced irrigation systems.
० Law: Hammurabi’s Code – first written law code.
० Trade: Extensive trade with India, Anatolia, and Egypt.
० Agriculture: Irrigation canals, ploughs, surplus food production.
० Education: Established scribal schools to train in cuneiform.
Q29. Basic Features of Roman Economy. (8 Marks)
Answer:
० Transport & Infrastructure: Well-built roads, ports, and ships encouraged commercial prosperity.
० Agriculture Dominated: Majority of Romans were peasants; agriculture was the backbone.
० Latifundia: Large estates run by slave labour produced surplus crops.
० Slavery: Slaves formed the base of production in agriculture, mining, and households.
० Trade & Commerce: Extensive trade network across the Mediterranean and with India/China via Silk Route.
० Urban Economy: Cities like Rome, Alexandria were major centers of craft production and trade.
० Currency System: Romans used a stable coinage system (denarius) which facilitated trade.
० State Revenue: Taxes from provinces and tributes enriched the empire.
OR – Social Categories of the Roman Empire. (8 Marks)
Answer:
० Patricians vs. Plebeians: Early distinction; patricians were aristocrats, plebeians were commoners.
० Senatorial Class: Richest and most powerful, held high offices and owned large estates.
० Equestrian Class (Knights): Wealthy, engaged in business, finance, and trade.
० Plebeians (Common Citizens): Small farmers, artisans, shopkeepers, soldiers; formed the backbone of the empire.
० Freedmen: Former slaves who had been freed; worked in various trades and services.
० Slaves: Large population, no rights, worked in fields, mines, and households.
० Women: Lacked political rights but could own property and run businesses in some cases.
० Citizens vs. Non-Citizens: Citizenship gave special rights; non-citizens had limited privileges.
Q3. Reasons for the Decline of Feudalism. (8 Marks)
Answer:
० Church Weakening: Decline of papal authority reduced the ideological base of feudalism.
० Growth of Towns & Trade: Rise of towns weakened rural feudal bonds.
० Money Economy: Use of money reduced dependence on feudal dues.
० Rise of Monarchies: Kings grew powerful, weakening feudal lords.
० The Crusades: Opened trade routes, promoted cultural contacts, reduced feudal isolation.
० Black Death (Plague): Wiped out one-third of Europe’s population, leading to labour shortages.
० Peasant Revolts: Peasants demanded freedom from feudal dues.
० Decline of Knighthood: Introduction of gunpowder and standing armies reduced importance of knight.
OR – Main Features of the Life of the Third Social Class of Medieval Europe. (8 Marks)
Answer:
० Gradual Change: With growth of towns, some peasants gained freedom and became independent farmers or merchants.
० The Third Estate: Included peasants, artisans, traders, and serfs – majority of population.
० Peasants’ Life: Worked on lords’ lands; gave rent, labour, and services.
० Serfs: Bound to the land, had no freedom to leave without lord’s permission.
० Hardships: Lived in poverty, faced famines, heavy taxes, and harsh justice.
० Craftsmen & Traders: Lived in towns; organised into guilds for protection.
० Role in Economy: Produced food and goods that sustained the feudal structure.
० Religion: Deeply influenced by Church teachings, festivals, and rituals.
SECTION – D (Source-based)
Read the following passages and give the answers of every question.
Q31. Income of The Roman Aristocracy, Early Fifth Century
‘Each of the great houses of Rome contained within itself everything which a medium-sized city could hold, a hippodrome, fora, temples, fountains and different kinds of baths… Many of the Roman households received an income of four thousand pounds of gold per year from their properties, not including grain, wine and other produce which, if sold, would have amounted to one-third of the income in gold. The income of the households at Rome of the second class, was one thousand or fifteen hundred pounds of gold.’
(A) This article is concerned with which thing? (1)
(B) What the position of high families in Rome? (1)
(C) Many Roman families had a high income. Explain by giving example? (2)
Q32. Estimated Extent of Mongol Destruction
All reports of Genghis Khan’s campaigns agree at the vast number of people killed following the capture of cities that defied his authority. The numbers are staggering: at the capture of Nishapur in 1220, 1,747,000 people were massacred while the toll at Herat in 1222 was 1,600,000 people and at Baghdad in 1258, 800,000. Smaller towns suffered proportionately: Nasa, 70,000 dead; Balhaq district, 70,000; and at Tun in the Kuhistan province, 12,000 individuals were executed.
How did medieval chroniclers arrive at such figures? Juvaini, the Persian chronicler of the Ilkhans stated that 1,300,000 people were killed in Merv. He reached the figure because it took thirteen days to count the dead and each day they counted 100,000 corpses.
(A) What was the policy of Genghis Khan for the cities which did not accept his supremacy? (1)
(B) Give any two examples in this regard? (2)
(C) How did Juvaini estimate the number of people killed in Merv? (1)
Q33. In Benedictine monasteries, there was a manuscript with 73 chapters of rules which were followed by monks for many centuries. Here are some of the rules they had to follow:
Chapter 6: Permission to speak should rarely be granted to monks.
Chapter 7: Humility means obedience.
Chapter 33: No monk should own private property.
Chapter 47: Idleness is the enemy of the soul, so friars and sisters should be occupied at certain times in manual labour, and at fixed hours in sacred reading.
Chapter 48: The monastery should be laid out in such a way that all necessities be found within its bounds: water, mill, garden, workshops.
(A) Who were expected to follow the above rules? (1)
(B) How should the monasteries be built? (2)
(C) What is humility in your point of view? (1)
SECTION – E (Map Based)
Q34.1. Mesopotamia Map – Identify:
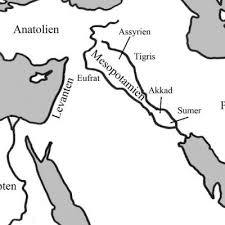
A – Ur, B – Uruk, C – Babylon.
Q34.2. Mongol Empire Map – Locate any two:
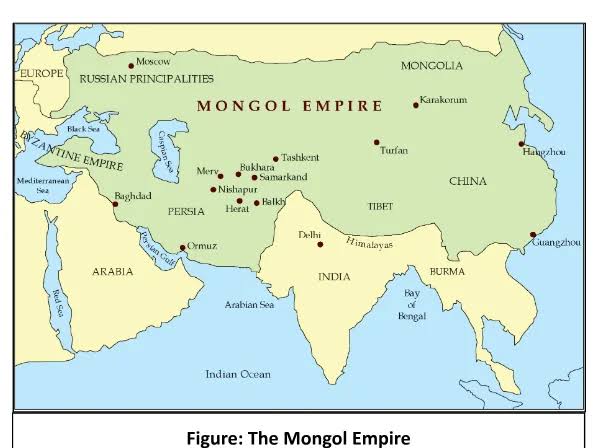
- Herat
- Bukhara
- Samarkand
Visually Impaired Alternative:
34.1. Three Mesopotamian cities: Ur, Uruk, Babylon.
34.2. Two Mongol Empire cities: Herat, Samarkand.








Very good