📘 Chapter 7 – An Imperial Capital: Vijayanagara
🔰 Introduction
- Vijayanagara = “City of Victory”, founded in 1336 CE by Harihara and Bukka of the Sangama dynasty.

- Located on the banks of Tungabhadra River, in present-day Karnataka.
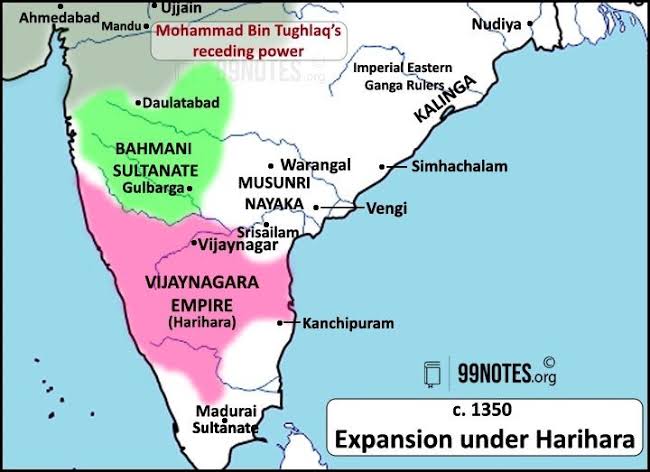
- Served as the capital of a powerful South Indian empire until its defeat in 1565.
- Impressive architecture, temples, and urban planning.
🏰 1. The Discovery of Hampi
- Hampi: Ruins of Vijayanagara rediscovered by Colin Mackenzie in 1800.

- Hampi is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Important sources:
- Archaeological evidence (monuments, temples, forts).
- Foreign travelers’ accounts (e.g., Abdur Razzaq, Domingo Paes, Nicolo Conti, Fernao Nuniz).

- Literary works and inscriptions.
🧱 2. The Vijayanagara Empire: Dynasties
- Four dynasties ruled:
- Sangama Dynasty (1336–1485)
- Saluva Dynasty (1485–1505)
- Tuluva Dynasty (1505–1570) – Most famous ruler: Krishnadeva Raya
- Aravidu Dynasty (1570–1646)
👑 3. Krishnadeva Raya (1509–1529): The Greatest Ruler

- Belonged to Tuluva dynasty.
- Expanded empire through military campaigns against Orissa, Bijapur, and Golkonda.
- Patron of literature and temple architecture.
- Wrote the famous Telugu work “Amuktamalyada”.
- Supported scholars in multiple languages – Sanskrit, Kannada, Tamil, Telugu.
🛡️ 4. Strain and Decline
- In 1565, a coalition of Deccan Sultanates defeated Vijayanagara in the Battle of Talikota.
- City was looted and destroyed.
🏛️ 5. Features of the City of Vijayanagara
a. Fortifications:

- Massive walls built with interlocking stones without mortar.
- Seven concentric fortification walls.
- Agricultural fields and residential areas were enclosed inside.
b. Agriculture and Irrigation:
- Used canals, tanks, and wells.
- Most notable tank: Kamalapura tank.
- Irrigation supported urban population and markets.
🕌 6. Temples and Architecture
a. Religious Buildings:
- Temples were cultural and economic hubs.
- Massive gopurams (gateway towers).
- Examples:
- Virupaksha Temple

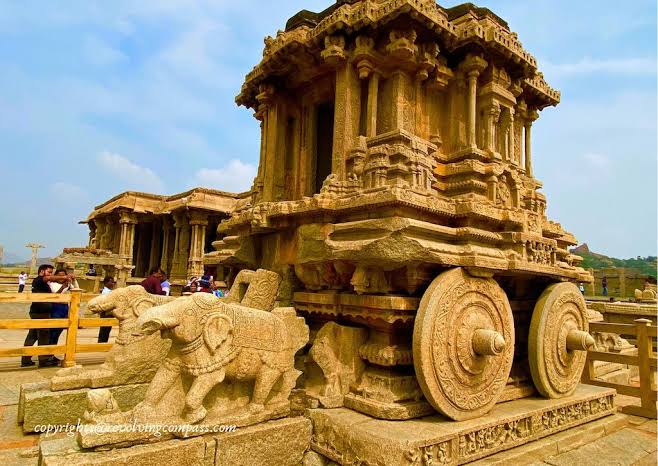
- Vittala Temple (famous for Stone Chariot and musical pillars)

b. Mandapas (Halls):
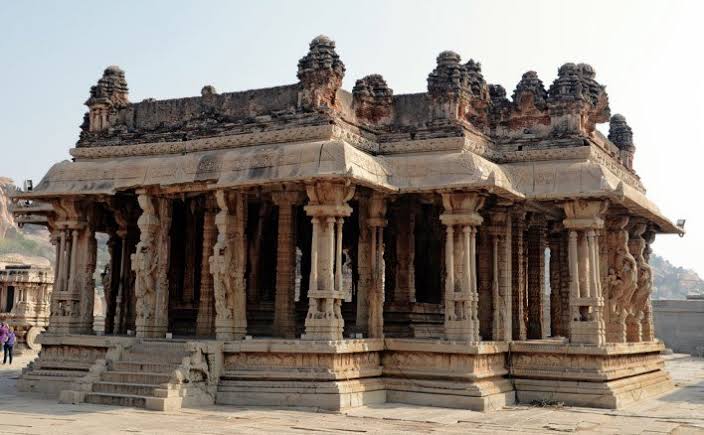

- Large halls used for ceremonies, marriages, performances.
- Ranga Mandapa: Pillared halls with sculptures of dancers and musicians.
🏘️ 7. Royal Centre and Sacred Centre
- Royal Centre:
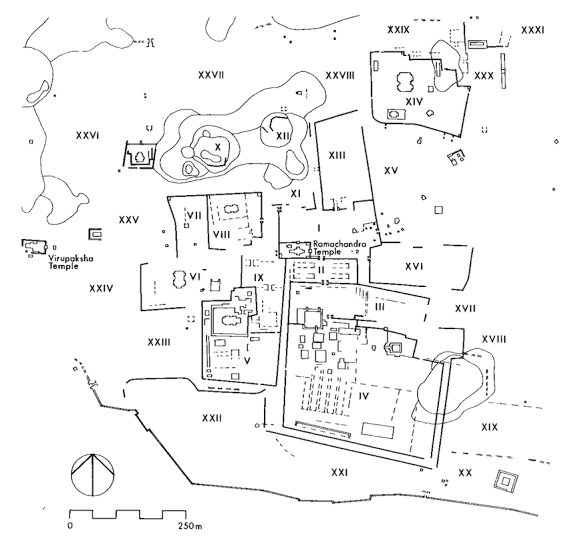
- Enclosed within fort walls.
- Contained palaces (e.g., Mahanavami Dibba,
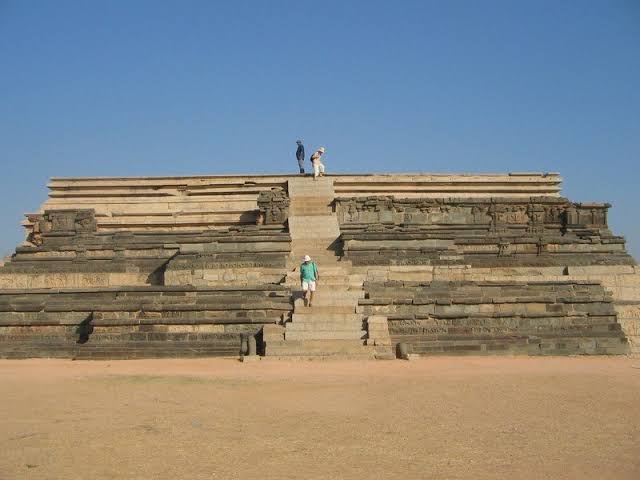

- Lotus Mahal,

- Hazara Rama Temple.

- Used for ceremonies, meetings, and royal durbars.
- Sacred Centre:
- Located along the Tungabhadra river.
- Contained important temples like Virupaksha, Vittala, and Krishna Temple.
🏯 8. Palaces and Courtly Architecture
- Mahanavami Dibba: Large platform used by kings to watch navaratri celebrations and military parades.
- Lotus Mahal: Arched palace with Indo-Islamic architectural influence.
- Hazara Rama Temple: Has Ramayana scenes carved on its walls.
📚 9. Sources of Information
- Foreign Travelers:
- Abdur Razzaq (from Herat): Described the grandeur and fortifications.

- Domingo Paes

- and Fernao Nuniz (Portuguese):

- Gave detailed accounts of court life, economy, festivals.
- Inscriptions and texts:
- Rayavachakam and Amuktamalyada
- Temple donations, land grants.
🧑🌾 10. Social and Economic Life
- Caste-based society.
- Agriculture was main occupation.
- Artisans, traders, temple servants.
- Active trade with Portuguese, Arabs, and other South-East Asian countries.
🎭 11. Rituals and Ceremonies
- Festivals like Mahanavami/Navaratri celebrated with grandeur.
- Military parades, music, dance, feasts.
🪔 12. Urban Planning and Trade
- Well-planned markets near temples.
- Markets sold precious stones, textiles, horses, etc.
- Hampi was a major trade hub.
🔚 13. Decline of Vijayanagara
- Defeat at Battle of Talikota (1565) by Deccan Sultanates (Bijapur, Ahmadnagar, Golconda, Bidar, Berar).

- City destroyed and never regained former glory.
📌 Conclusion
- Vijayanagara was a political, cultural, and economic powerhouse.
- Today its ruins serve as evidence of India’s rich medieval urban and architectural heritage.
- Crucial for understanding the fusion of temple culture, trade, and administration.
📚 Important Terms
- Gopuram – Monumental entrance tower of a temple.
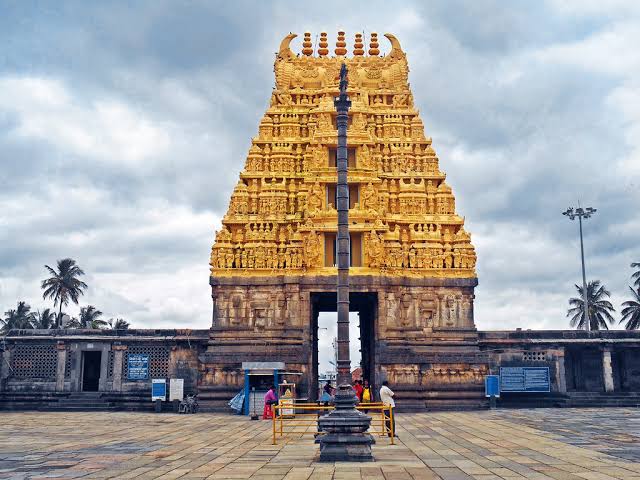

- Mandapa – Pillared hall in a temple.
- Mahanavami Dibba – Royal viewing platform.
- Amuktamalyada – Telugu text by Krishnadeva Raya.
- Rayavachakam – Text that mentions rituals and court practices.







